

Building A Carport – Comprehensive Guide 2023
- Kunal Singh
“Steel and Stud” can help you go a long way in building and installing carports in the US. Their affordability and accessibility make them suitable for building carports for your vehicle safety. The guide is for everyone who wants to build their carport plans. But first, It’s important to know the type of carport you want to build.
Table of Contents
Types of Carport
Let’s look into various types of carports:
Open-Sided Carports
An open-sided carport can also function as a two-car carport for those not keen to install add-ons such as shelves or cabinets. Their cost-efficiency makes them an instant hit amongst vehicle owners.

Enclosed Carports
Enclosed structures don’t just guarantee great property value but also protect vehicles throughout the year. If you live in a windy area, this option might be perfect for your multiple vehicles, even if the project can border on labor-intensive.
You can obtain more information from our expert guide on How to enclose a metal carport.

Portable Carports
A basic freestanding carport comes in handy if you are one of those vehicle owners who don’t need to ensure vehicle protection throughout the year. A metallic or stainless steel freestanding structure can quickly assemble and disassemble.
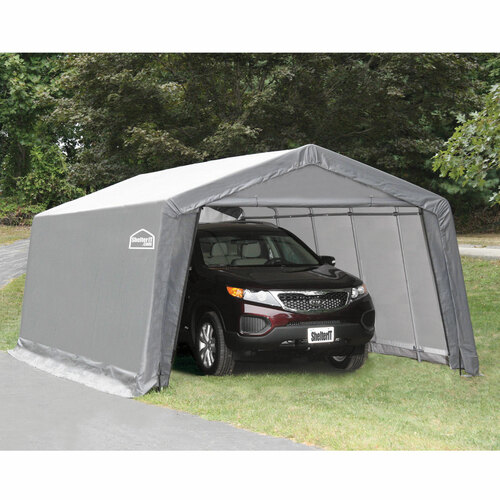

Factors to Consider Before Building A Carport
Some of the significant factors to consider before building a carport include the following:
- Size: Before metal carport installation, it is advisable to check the size of your vehicles. This will help you understand how much space you will need.
- Cost: You must always consider the cost of building the carport. The metal carport cost would significantly vary depending on the size. The bigger the size, the higher the cost.
- Building Permit: While installing the carport, you will need building permits. This is to determine the compliance and safety of the structure. It is advisable to consult your neighborhood homeowners association for better details.
- Foundation: A carport’s foundation should be solid. It should provide stability and require low maintenance. Gravels are the most preferred option for laying the foundation of your metal carport. This will provide strength to the metal carport wall.
Steps to Building A Carport
1. Prepare the Ground
You can pick the appropriate building materials depending on whether you wish to assemble a carport from metal or wood and the climatic conditions where you live. Then the first step is to prepare the ground for the base.
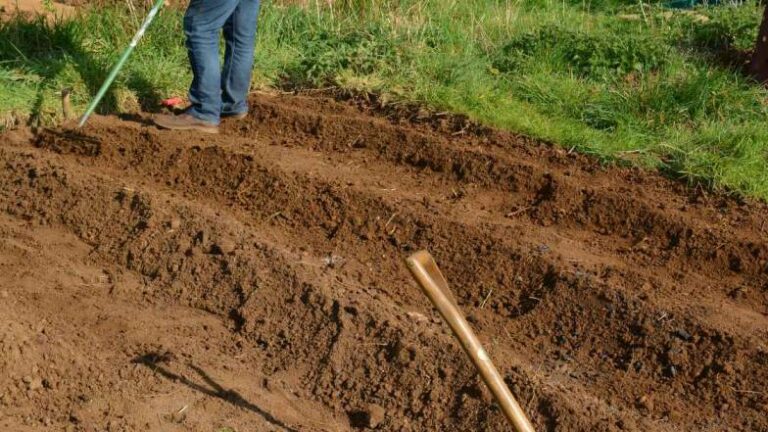

a. Measure the ground: To park an average-sized car on your property, you must plot a rectangle at least 16 feet long and 9 feet wide. Basic free carport plans will need a rectangular plot of land meant for building such a structure that should have six posts.
b. Level the ground if you deem it necessary: You must level ground for carport with a shovel if you decide to install a metal carport on a concrete pad next to your house. Make sure the ground is as even as possible and given that you are nowhere near buried lines, apply foot pressure and remove grass, if any.
c. Pour ground cover; if necessary: Getting a post fixed to bare grounds can be a good idea, but you would have to resort to getting some crushed granite or gravel for some curb appeal. For a high-satisfaction project, try pouring some concrete instead,
2. Building the Beams

a. Dig the holes for the posts: Once you are all set with a place to build your own carport, the next step is to secure support posts. Ensure the holes are at least 2 feet deep and 6 feet under the frost line. If you reside in a windy or snowy area, make holes at least 4 feet deep to secure support posts that will give your carport a more stable structure.
b. Set the six posts: For a slanting roof, you must have three posts at least 9 feet high to put on one side of the carport and another three at least 11 feet high. After filling the hole up to six inches with concrete, position the post so it is vertical and can rest on the bottom. Make sure you use a leveling tool to make the surface even as the concrete hardens.
c. Fasten the front and back beams first: Build a rectangular box of dimensions 16 feet x 9 feet x 7 feet. T-shape hangers that are available in any hardware store can help you affix the supporting crossbeams to the higher posts.
d. Fasten the side beams: Try to secure the structure as much as possible, primarily if you reside in an area with severe climatic conditions.
3. Building the Carport Roof

a. Fasten the rafters to the side beams: Fix six rafters of 2″ x 4″ x 10′ dimensions such that they support the roof. Both ends of rafters must be fastened with the support beams at the front and back.
b. Notch the rafters: Rest the rafters along the straight edge of the support beams. This method might not come in handy if you wish for the rafter to remain in close contact with the beams.
c. Hang the rafters: You will require metal joist hangers for this method. Rafters must be affixed to the support beams at an angle of about 25 degrees. In the hanger method, the rafters would remain atop the beams.
d. Fasten the steel sheet roof to the rafters: As opposed to building a carport using wood, where getting some plywood sheets would be the next part of your project, in the case of metal carports, you would need to fasten a galvanized steel sheet to construct the roof.
4. Finishing the Job
To avoid exposed wood that compromises the car protection offered by the carport, cover the roof with tar paper to ensure you have got a waterproof surface. Nail metal plates into the joints, especially with gaps between beams, posts, and rafters, for enhanced stability.
How to Build A Carport for 2 Cars

- For successful results, the first step to building a two-car carport is to lay out your carport plans. Use string and batter boards, apply the 3-4-5 rule and see that the diagonals are accurate and that it’s all right-angles.
- Anchor the posts using metal anchors and concrete footing. When it’s time to install posts, plumb them with a spirit level.
- Once you have fixed the support beams, use 4×4 lumber to build braces and cut the ends at 45 degrees. Reinforce the carport frame with these braces, and then you can drill the pilot holes.
- Assemble the beams on a level surface so that you can cut the materials appropriately and lock them together with screws. Bottom rafters and common rafters must be built from 2×6 lumber and 2×4 lumber, respectively.
- Install the trusses, fit the gable ends, work with the overhangs, and then fix the roofing sheets. After aligning the metal sheets, affix them to rafter panels such that there are no gaps between the sheets.
- The last step is to cover the shed with roofing felt or tar paper.
Building a carport on the boundary? What you Need to Know
Based on your place of residence, you will have to comply with certain rules and regulations to begin working on your carport close to the boundary wall.
It’s recommended that you consult the local council first before proceeding with your carport kit installation. You could browse their official websites to get an idea about what you can expect.
Cross-check with the builder and ensure all the certifications, licenses, and permits are in place before setting your project in motion.
Get in touch with a professional tree-feller to take care of the trees and vegetation surrounding the chosen area.
When creating a design outline for carports on the boundary, drainage positions and stormwater areas must be considered. The slope’s descent would determine whether or not you must cut deeper into the land and oversee further leveling.
Building The Carports- Rules and Requirements to Abide
Before you act on your carport project, you must ensure that you meet all the building codes for your municipality, state, city, or county. These codes include structural codes, accessibility codes, building/dwelling codes, plumbing codes, energy codes, mechanical codes, electrical codes, fire/life safety codes, and elevator codes for each state.
Building/ dwelling codes usually include smoke alarms, ground fault circuit interrupters, beams and joists, rescue openings or emergency exits, ladders, steps, and windows. Structural codes set forth the structural standards for building work. Similarly, electrical codes establish a set of standards that facilitate the safe installation of electrical equipment and wiring in the US. The fire and life safety codes protect people from occupational and fire-related hazards.
Every city has its own set of codes, so visit your city’s municipal office to ensure that your building plans align with their requirements. If you reside in a neighborhood supervised by a homeowners association, you have to discuss your plans with them as well.
Is it Possible to Build a carport without a permit?
Municipalities of most cities in the US would expect their law-abiding citizens to get approval for building a carport. In some cases, you can be asked to pay a hefty sum of money, which can be double or triple the fine you would have had to pay in the case of a missing permit.
A portable or temporary carport can be an exception to this law. Since these can be moved around and don’t need to be fixed to a concrete slab, the city doesn’t seem to mind if you have one of these permit-free.
Your intention might be to build a permanent carport, and you know it’s not going to be a living space, but even then, if the county expects you to follow all the necessary codes, then you must. Otherwise, you could be risking getting your permit suspended.
Materials Required for Building A Metal Carport

Some basic tools to set up a carport are a ladder, measuring tape, hammer, shovel, string line, hand saw, adjustable wrench, carpenter’s square, spirit level, and G-clamps. Important power tools you need for the project include a rivet gun, angle grinder, hammer drill, circular saw, and nail gun. Those planning on a wooden structure would have to invest in pressure-treated lumber. Other items are metal anchors, steel rods, shingles, roof covers, bolts, T-hangers, anchor bolts, joist hangers, and concrete mix. Add solar panels to your list if you are searching for an option that will let you charge your electric but eco-friendly car.
Average Cost to Build a Wooden and Metal Carport in 2023
Metal carports are affordable and accessible in the pocket compared to wood carports. The average custom metal carports price per sq. ft. is $15 – $30, and for wood carports are $20 – $30. The average prefab rate per sq. ft. for metal carports is $10 – $15, and for wood, carports are $15 – $20.
5 Tips for Building A Steel Carport with Ease
- Apply for permits if necessary at the earliest. Getting approval for your project can take days or even weeks, so you must submit the forms way ahead of your building schedule.
- While leveling the ground before digging holes, you have to make sure with professional guidance that your project wouldn’t interfere with utility lines, such as sewer, gas, or water lines.
- Having a carport plan is quite important. You can go through free plans to get a rough idea first and then go for a paid one if you consider it necessary.
- As a durable option, steel carports are becoming increasingly popular these days. A metal frame can offer extra stability and guarantee protection to your car during heavy snow, flooding, or windy days.
- Align your posts properly. In areas with frequent soil erosion, dig holes deeper than two feet.
Maintenance and Care of the Carport
The metal carport is one of the most significant investments, so it is necessary to take care of it properly. Proper care and maintenance of the carport maintain functionality and ensure longevity. Here are some of the significant tips and tricks to follow for maintaining and caring for the carport:
- Keep it clean always: Spot cleaning and deep cleaning are extremely crucial because it helps to keep the carport clean. There is always a risk of oil spills, so metal deep cleaning is required.
- Remove debris from the roof: When leaves and debris accumulate on the metal carport roof, it traps the moisture leading to an increased risk of corrosion. Therefore, removing leaves and debris as soon as you watch it accumulate is advisable. Furthermore, if you notice any spots on your roof, wash it using water and soap.
- Make repairs: If you check your metal carport roof often, you may notice minor wear and tear. In this case, you can make the repairs soon. You should also make the repairs in case the color chips away to maintain an attractive carport.
- Prevent moisture damage: Moisture damage can be hazardous for your carport. It will lead to rust, thereby affecting the strength of the metal building. Thus, make sure to prevent moisture damage as much as possible.
Safety Considerations
- Ensuring structural integrity: Using good quality materials, fasteners, and proper assembly is essential. You must never compromise on the structure’s strength, mainly through regular maintenance and inspection.
- Fire safety: Although metal carports are fireproof, it is advisable to avoid keeping any inflammable substance around the carport. Furthermore, you must ensure the electric wiring adheres to the safety and building codes.
- Weatherproofing and protection against natural elements: It is advisable to apply weather-resistant coatings to improve durability. Furthermore, choosing the right carport design can protect against damage due to strong winds and heavy rain.
If you feel less sure about your project or face a mishap while working with the middle post or support beams, or if you cannot get a post fixed, Steel and Stud can help you ease your troubles. Hiring the best in the industry can be the perfect solution to make your carport building process easy and successful.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, a permit is necessary to construct a carport. For this, you must produce a site plan indicating the carport’s position and how close or far it is from the property lines.
A pre-fabricated carport can be the right step in the DIY carport building direction. For perfect carport maintenance, employ spot cleaning and deep cleaning, remove leaves and debris that builds up on the roof during fall, and make repairs whenever necessary.
Buying a metal or steel carport will be easier on the pocket than building one right from scratch.
A carport can be considered a garage without walls, doors, or windows. Turning a carport into a garage is undoubtedly feasible.
Finding the perfect carport is a challenging task. Researching and checking all the factors that will help you get the right carport is advisable. These include the following:
- Size: It is always important to check the size of your carport and the available size in your house for easy installation.
- Roof: The metal roofing of the carport is essential in determining aesthetics and functionality.
- Color: Metal carport building not only provides aesthetics but also prevents rust.
The cost of building the 20×20 carport can range from $4,000-$10,000, depending on your requirements.











Indoor Riding Arenas: Types, Features, Benefits, and Cost



Different Types of Metal Roofing for Commercial and Residential Buildings



What Is A Purlin? Types, Sizes, Designs, Accessories & Cost


